Eco-Friendly Plumbing Upgrades and Water Conservation: Regulations and Best Practices in Canada
As environmental concerns grow, homeowners and businesses across Canada are increasingly focusing on sustainability in their renovation and repair projects. Plumbing systems, a critical component of any building, offer significant opportunities for improving water efficiency and reducing environmental impacts. By adopting eco-friendly plumbing upgrades and adhering to water conservation regulations, Canadians can reduce water waste, lower utility bills, and help preserve the country’s natural resources. This article explores the key regulations and best practices for eco-friendly plumbing upgrades in Canada, along with practical ways to enhance water conservation in homes and buildings.

The Importance of Water Conservation
Water conservation is becoming an urgent issue in many parts of the world, including Canada, where rapid urbanization and changing climate patterns are placing increasing pressure on freshwater supplies. Efficient use of water resources is essential to maintaining the country’s ecosystems, reducing the strain on infrastructure, and minimizing energy consumption related to water heating and treatment.
Eco-friendly plumbing upgrades play a key role in promoting water conservation by reducing waste, improving efficiency, and lowering the energy footprint of buildings. These upgrades include the installation of low-flow fixtures, greywater systems, rainwater harvesting technologies, and efficient hot water systems.

Key Eco-Friendly Plumbing Upgrades
1. Low-Flow Fixtures and Faucets
Low-flow plumbing fixtures are designed to reduce water consumption without compromising performance. Common low-flow upgrades include:
- Low-flow toilets: Traditional toilets use about 13 liters of water per flush, whereas low-flow models use only 4.8 to 6 liters per flush, significantly reducing water waste.
- Low-flow showerheads: These reduce water flow from an average of 9.5 liters per minute to as low as 5.7 liters per minute, saving thousands of liters of water annually without impacting water pressure.
- Low-flow faucets: Designed to reduce water flow while maintaining a steady stream, these fixtures can cut water use by 30-50% compared to standard faucets.
In Canada, many provinces and municipalities encourage the use of low-flow fixtures through regulations, and in some cases, financial incentives are offered for upgrading to more water-efficient systems.
2. Greywater Systems
Greywater is wastewater generated from sources like sinks, showers, and washing machines (excluding water from toilets). Greywater systems treat and reuse this water for purposes such as toilet flushing and landscape irrigation, reducing the demand for fresh water and minimizing wastewater output.
By installing a greywater recycling system, property owners can save up to 30-50% of their potable water use. This is particularly beneficial in areas where water conservation is a priority, such as drought-prone regions of Canada.
Greywater systems must meet strict health and safety standards, particularly in urban areas, to ensure that recycled water is safely reused. In provinces like British Columbia and Ontario, building codes set guidelines for the design, installation, and maintenance of greywater systems to ensure public health is protected.
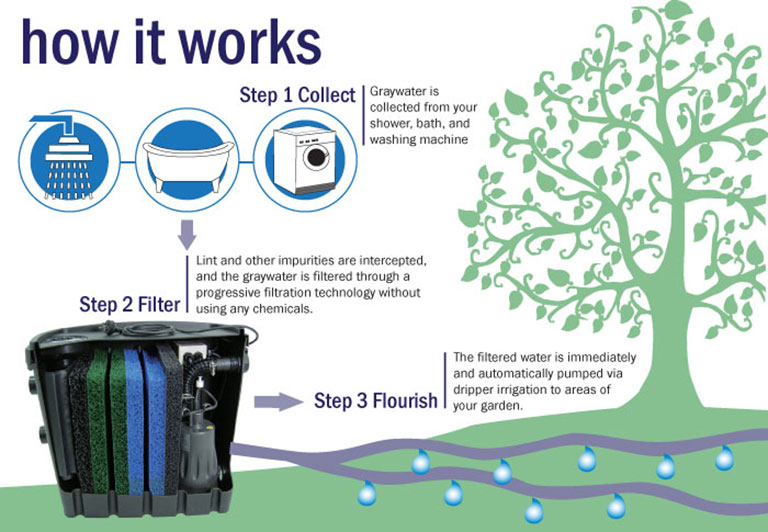
3. Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Rainwater harvesting systems collect and store rainwater for non-potable uses, such as irrigation, toilet flushing, and even laundry in some cases. This reduces reliance on municipal water supplies, especially during periods of water shortages or drought.
Rainwater harvesting is an eco-friendly plumbing upgrade that not only conserves water but also helps manage stormwater runoff, which can overwhelm urban drainage systems and contribute to flooding. Rainwater systems are subject to regulations that ensure safe and efficient storage, filtration, and distribution of rainwater. Many Canadian municipalities offer rebates or incentives to homeowners and businesses that install rainwater harvesting systems.
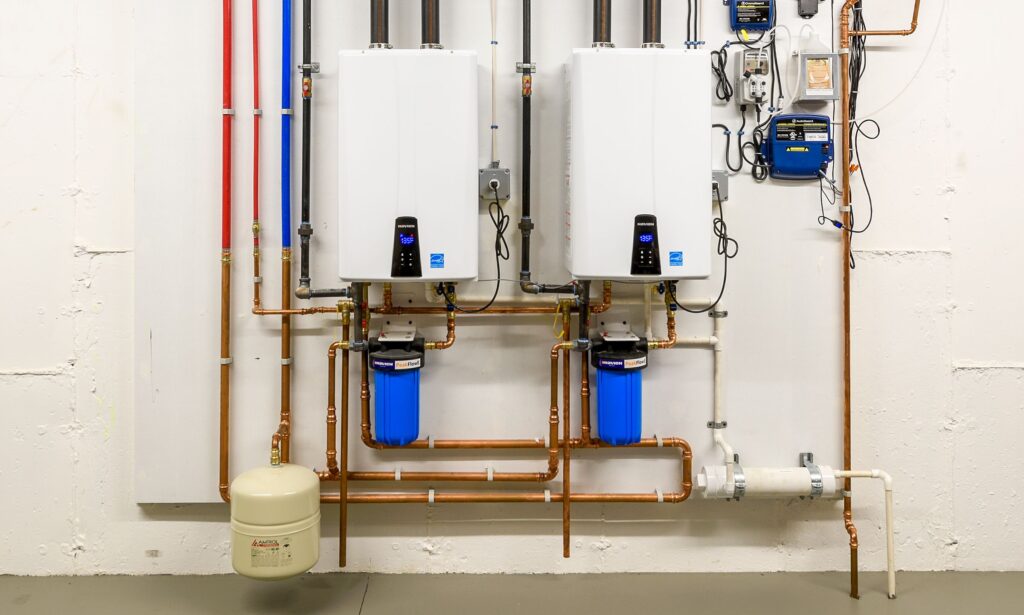
4. Tankless Water Heaters
Traditional water heaters continuously heat large volumes of water, even when it’s not needed, leading to energy waste. Tankless water heaters, on the other hand, heat water on demand, reducing energy consumption and water waste.
By upgrading to a tankless water heater, homeowners can enjoy endless hot water while using less energy, contributing to a reduction in both utility costs and carbon emissions. In provinces like British Columbia and Ontario, building codes promote the use of high-efficiency water heaters to support Canada’s overall energy reduction goals.

Water Conservation Regulations in Canada
Water conservation efforts in Canada are governed by a combination of federal, provincial, and municipal regulations. These regulations aim to reduce water consumption, manage wastewater more effectively, and promote eco-friendly plumbing practices.
1. National Plumbing Code of Canada
The National Plumbing Code of Canada (NPC) sets minimum standards for plumbing systems in buildings. It includes provisions related to water efficiency, such as the use of low-flow fixtures and high-efficiency water heaters. The NPC is updated regularly to reflect advances in technology and environmental standards, ensuring that buildings in Canada meet modern requirements for water conservation and sustainability.
Each province adopts and modifies the NPC according to its specific needs, so homeowners and contractors should consult their local building codes to ensure compliance with water conservation regulations.
2. Provincial Water Conservation Standards
Many provinces have developed additional standards and initiatives to promote water conservation and encourage eco-friendly plumbing upgrades. For example:
- British Columbia: BC’s Water Sustainability Act regulates water use and encourages conservation measures, particularly in urban areas and regions prone to drought. Building codes in BC also promote the use of greywater recycling and rainwater harvesting systems in both residential and commercial properties.
- Ontario: Ontario’s Water Opportunities and Water Conservation Act aims to make the province a leader in water efficiency. The province’s building code includes stringent requirements for low-flow fixtures and efficient water heating systems, as well as incentives for water-saving technologies.
3. Municipal Rebates and Incentives
To encourage the adoption of water-saving technologies, many Canadian municipalities offer rebates or incentives for eco-friendly plumbing upgrades. For instance:
- Toronto’s Basement Flooding Protection Subsidy Program offers homeowners financial incentives for installing sump pumps, backwater valves, and other flood prevention systems, which also help conserve water during periods of heavy rainfall.
- Vancouver’s Water Conservation Program promotes water-efficient appliances and offers rebates for the installation of rainwater harvesting systems and low-flow fixtures.
These local programs make it easier for homeowners and businesses to upgrade their plumbing systems while contributing to broader water conservation efforts.
Best Practices for Eco-Friendly Plumbing Upgrades
In addition to adhering to regulations, homeowners and businesses can implement best practices for plumbing upgrades to further enhance water conservation and efficiency. Here are a few key tips:
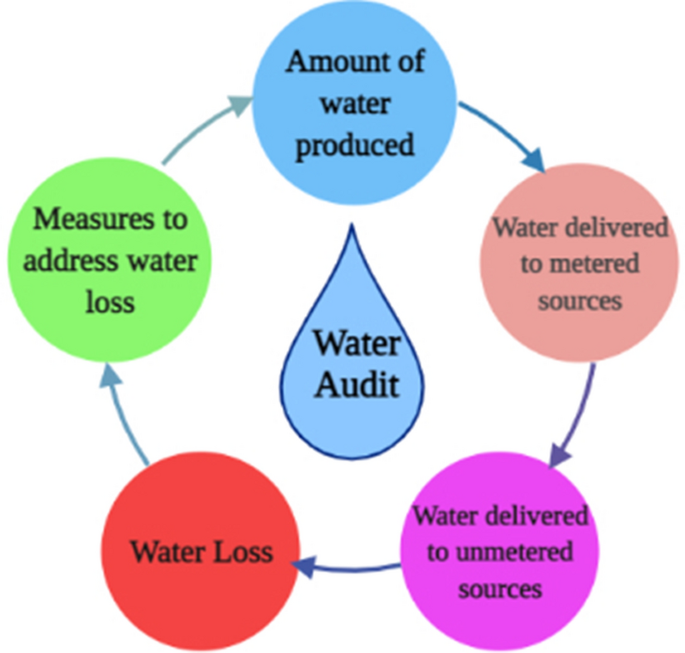
1. Conduct a Water Audit
Before making any plumbing upgrades, it’s helpful to conduct a water audit to determine where water is being used and where waste can be reduced. This audit can highlight inefficiencies in fixtures, leaks, and water heating systems, providing a roadmap for targeted upgrades.
2. Fix Leaks Promptly
Even small leaks can result in significant water waste over time. It’s essential to fix any plumbing leaks, such as dripping faucets or running toilets, as soon as they’re detected. Regular maintenance of plumbing systems can prevent leaks from occurring and ensure fixtures operate efficiently.
3. Install Smart Water Meters
Smart water meters provide real-time data on water usage, allowing homeowners and businesses to monitor consumption and identify areas where water can be conserved. These devices can also detect leaks and anomalies in water use, helping to prevent waste and damage to the property.
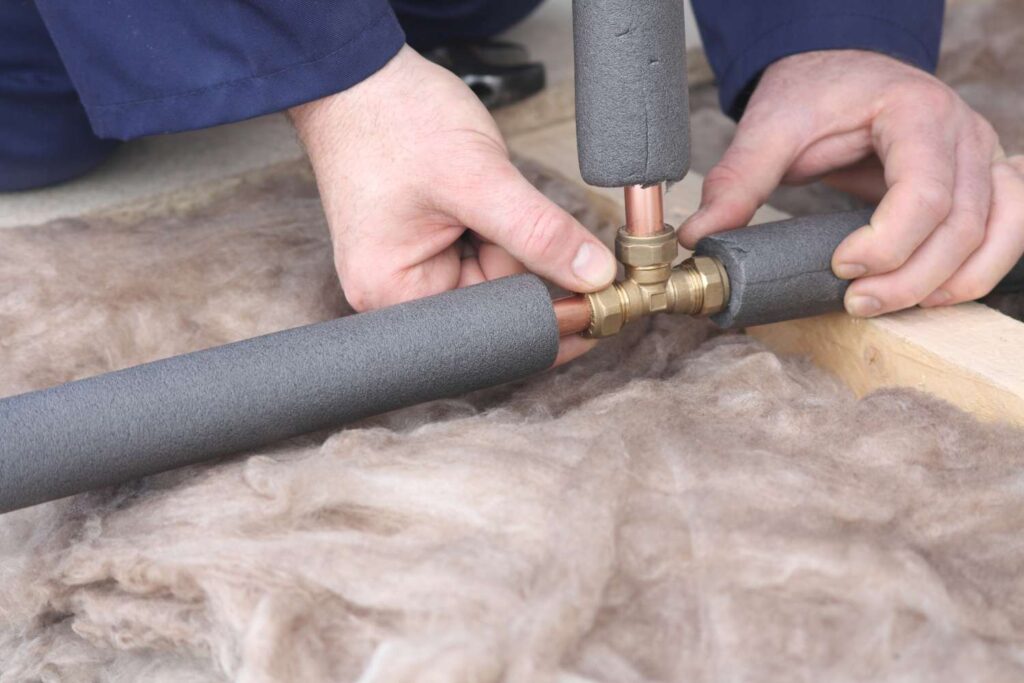
4. Insulate Pipes
Insulating hot water pipes reduces heat loss, meaning water will reach the desired temperature more quickly, which in turn reduces the amount of water wasted while waiting for hot water. This simple upgrade can increase energy efficiency and contribute to water conservation efforts.

Conclusion
Eco-friendly plumbing upgrades are an essential part of sustainable building practices in Canada. From low-flow fixtures to rainwater harvesting systems, these upgrades help conserve water, reduce utility costs, and support environmental goals. By adhering to national, provincial, and municipal water conservation regulations, homeowners and businesses can play a significant role in preserving Canada’s water resources for future generations.
